EGG COLLECTION PROCESS
EGG COLLECTION PROCESS
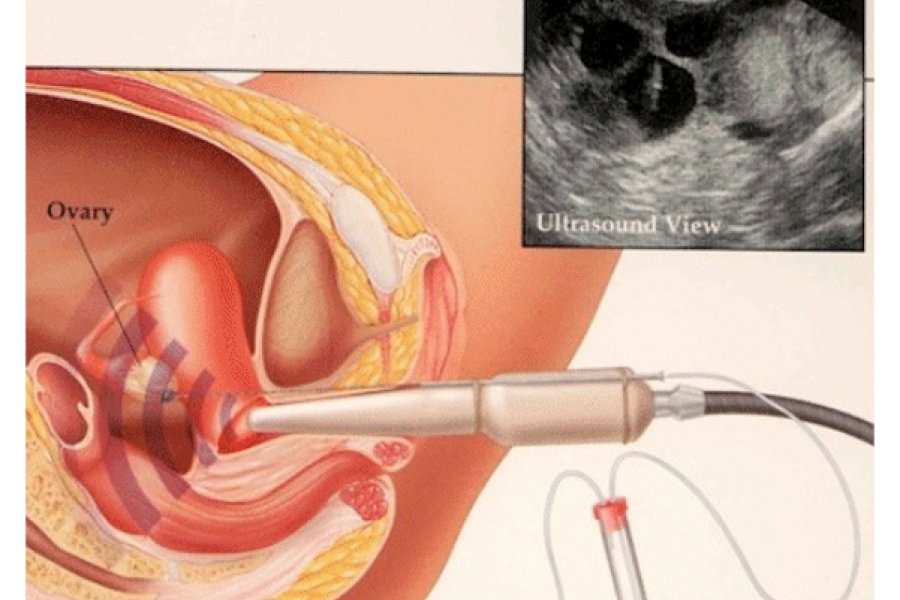
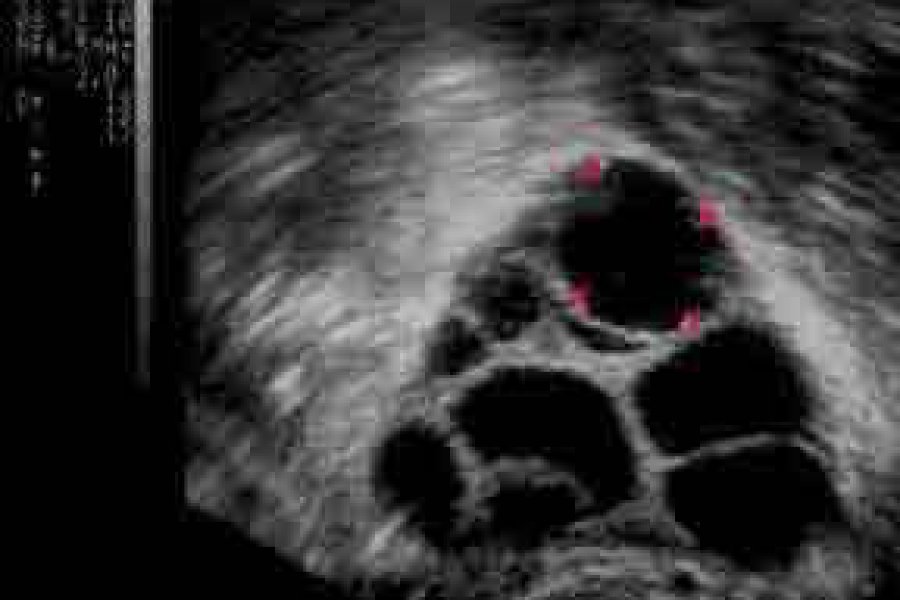
Egg collection is done 36 hours after the HCG hormone is administered. The patient is told to come to the hospital with his wife one hour before the procedure. Sperm is also taken from the husband before starting the egg collection process. Egg retrieval can be performed under general or local anesthesia. In any case, the patient should not take any food or drink until 6-8 hours before the procedure. The patient is taken to the operating room after urinating before the procedure. If the procedure will be performed under general anesthesia, the patient is put to sleep after the patient is positioned on the operating table. After the vagina is washed with physiological saline, the patient is covered with sterile drapes and the follicles in the ovaries are aspirated one by one with the help of ultrasound. The contents of the aspirated follicles are evaluated in the embryology laboratory and the eggs are taken and placed in the culture medium. In cases where the egg does not come from the follicle, the inside of the follicle can be washed and the egg can be obtained. All of the follicles in both ovaries are aspirated in turn. After the egg collection process is completed, the ovaries are evaluated with ultrasound, it is checked whether there is any active bleeding, it is observed whether there is a blood accumulation (parametrial hematoma) between the membranes around the uterus, and whether there is any bleeding into the Douglas cavity (back of the uterus). At the end of the procedure, the vagina is evaluated and it is checked whether there is any vaginal bleeding. If there is bleeding, a tampon is applied until it stops. If necessary, stitches can be placed to stop the vaginal bleeding. After the patient wakes up from general anesthesia, he is taken to the normal patient bed and if there is no problem after 2-4 hours of follow-up, the patient is discharged. After egg collection, the patient can be started on antibiotics and prednol. Vaginal or paraenteral (needle-shaped) progesterone hormone is started for luteal phase support that day or the next day after egg retrieval.
Complications that may occur during egg collection:
Bleeding
Bleeding may occur from the follicle wall, ovarian surface and vaginal mucosa, and blood may accumulate between the membranes surrounding the uterus (womb) (parametrial hematoma). Severe bleeding into the abdomen may occur as a result of the needle injuring the great vessels (illiac vessels).
Intra-abdominal organ injury
During egg collection, the needle may injure other organs (bowels and bladder) in the abdomen.
Infection
Pelvic infection and abscess may develop, especially in cases with hydrosalfenx or in cases where endometriomas are aspirated.
Complications related to the anesthesia procedure may occur.