Stimulating Ovulation
Stimulating ovulation (ovulation induction)
The most appropriate treatment protocol for the patient is determined by the IVF team that undertakes the treatment. The drugs to be used by the patient are determined and prescribed, and the patient is provided with the drugs. After starting the treatment, the drugs that the patient will use during the treatment are written in detail in the form of a daily calendar and given to the patient's hand and explained to the patient in a very clear and concise language.
Although there are many different treatment protocols, the most commonly used protocols are:
Long protocol (Long protocol)
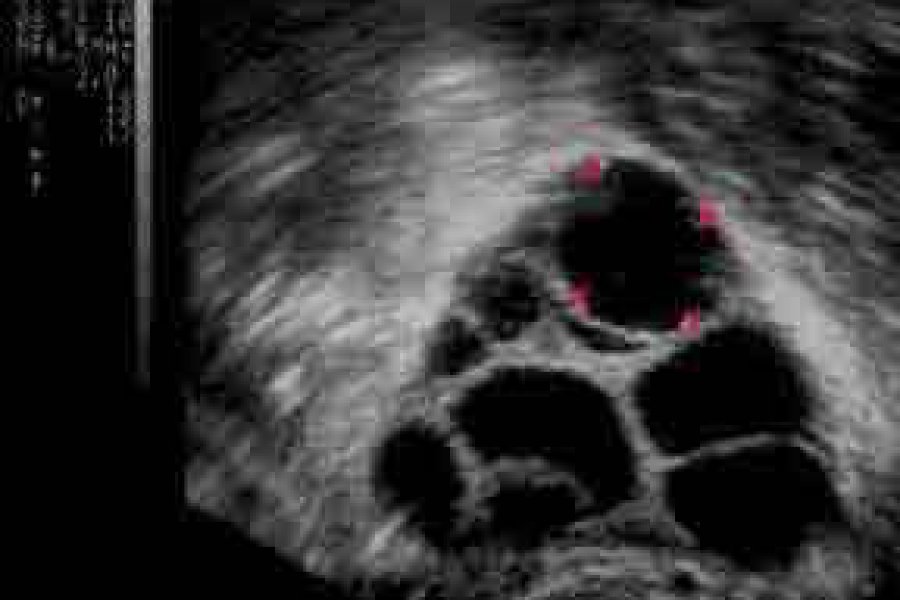
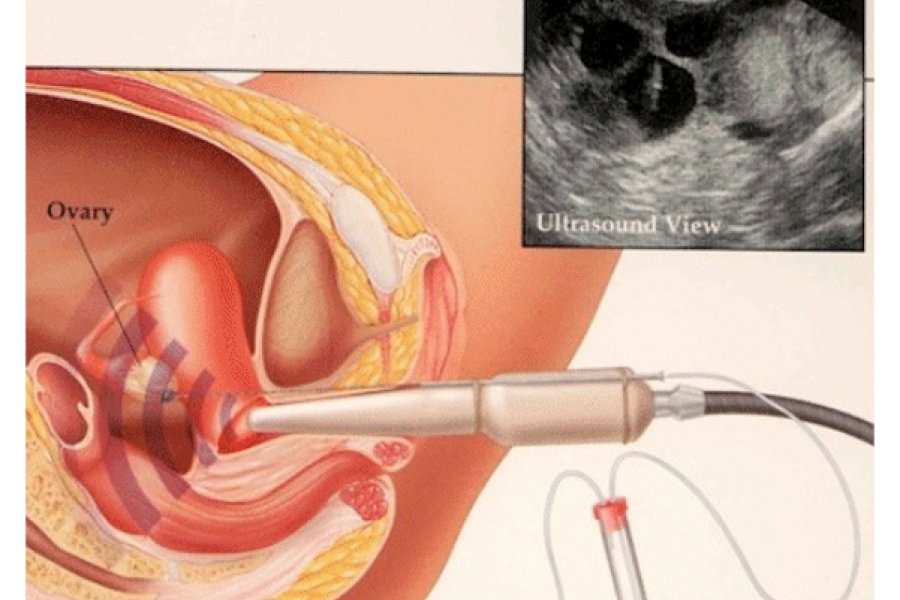
The long protocol is preferred in the patient group that responds normally to drugs. The treatment is started on the 21st day of the previous menstrual period, birth control pill can be given to the patient in the previous menstrual period and treatment can be started together with the birth control pill. The patient is started on a GnRH analogue on the 21st day. The GnRH analogue is used until the day before the egg retrieval (until HCG is made). If the patient has used birth control pills, birth control pills are used for 4 more days after starting GnRH. The patient's menstrual bleeding is expected to begin, and usually on the 3rd day of menstrual bleeding, ultrasound evaluation is performed and gonadotropin hormone is started at a predetermined dose. The patient is called for control after 5 days and the development of follicles (formations containing eggs) is evaluated by ultrasound, and if necessary, the patient's drug dose is adjusted by looking at the E2 hormone. Then, the patient is called for control at certain intervals (every other day or every other day), and follicle development is followed by ultrasound and, if necessary, E2 values. When the leading follicles reach a diameter of 17-18 mm, HCG hormone is administered and egg collection is performed 36 hours later.
antagonist protocol
The antagonist protocol is preferred in patients with a risk of hyperstimulation syndrome, such as "polycystic ovarian syndrome", where ovarian response is thought to be excessive. In the antagonist protocol, birth control pills can be used in the previous menstrual period. The treatment is started with gonadotropin hormone following the ultrasound examination on the 2nd or 3rd day of menstrual bleeding. The patient is called for control after 5 days and the development of the follicles (formations containing the egg) is evaluated by ultrasound and if necessary, the E2 hormone level is checked. When the follicle diameter and E2 hormone level reach certain values, GnRH antagonist is started. The antagonist is administered in daily doses. After the antagonist is started, the HCG hormone is continued until the day and the patient is called for control at certain intervals (every other day or every other day). Follicle development is followed by ultrasound examination and, if necessary, E2 hormone values. When the leading follicles reach a diameter of 17-18 mm, HCG hormone is administered and egg collection is performed 36 hours later. In the antagonist protocol, a GnRH analogue can also be used instead of the HCG hormone.
Protocols Suppressed with Progesterone Hormone
It can be applied in patients who will not be transferred fresh, where all embryos will be frozen or who will undergo egg freezing. Treatment is started with gonadotropin hormone following the ultrasound examination on the 2nd or 3rd day of menstrual bleeding. On the same day or the next day, oral progesterone hormone (duphaston or tarlusal) is started and the progesterone hormone is used until the egg is collected. The patient is called for control after 5 days and the development of the follicles (formations containing the egg) is evaluated by ultrasound and if necessary, the E2 hormone level is checked. The patient is called for control at certain intervals (every other day or every other day). Follicle development is followed by ultrasound examination and, if necessary, E2 hormone values. When the leading follicles reach a diameter of 17-18 mm, HCG hormone is produced and egg collection is performed 36 hours later. In protocols suppressed by progesterone hormone, GnRH analog can be used instead of HCG hormone.
Natural cycle (natural cycle)
It can be tried in the patient group with poor ovarian response, the egg formed without using any medication is collected following the administration of HCG hormone. Egg quality is generally good.
Apart from these, there are also modified protocols with aromatase inhibitors according to the patient's condition.
The ideal number of eggs is between 12 and 14, and the rate of conception is lower in patients with less than 5 eggs. In cases where the number of eggs is over 20, the risk of hyperstimulation is high. As the number of eggs increases, the cumulative pregnancy rates also increase.